The Canadian Light Source in Saskatoon has produced new high-resolution images that can help cannabis researchers determine the optimal harvest times for the plant. The images, which are being hailed as groundbreaking, were made possible by the use of the BXDS High Energy Wiggler Beamline and Mid-IR Beamline at the Canadian Light Source’s synchrotron. The research was led by Teagen Quilichini of the National Research Council, who explained that the long-standing prohibition on cannabis had severely limited the amount of research that had been done on the plant.
Top Products: Assuage Sunshine
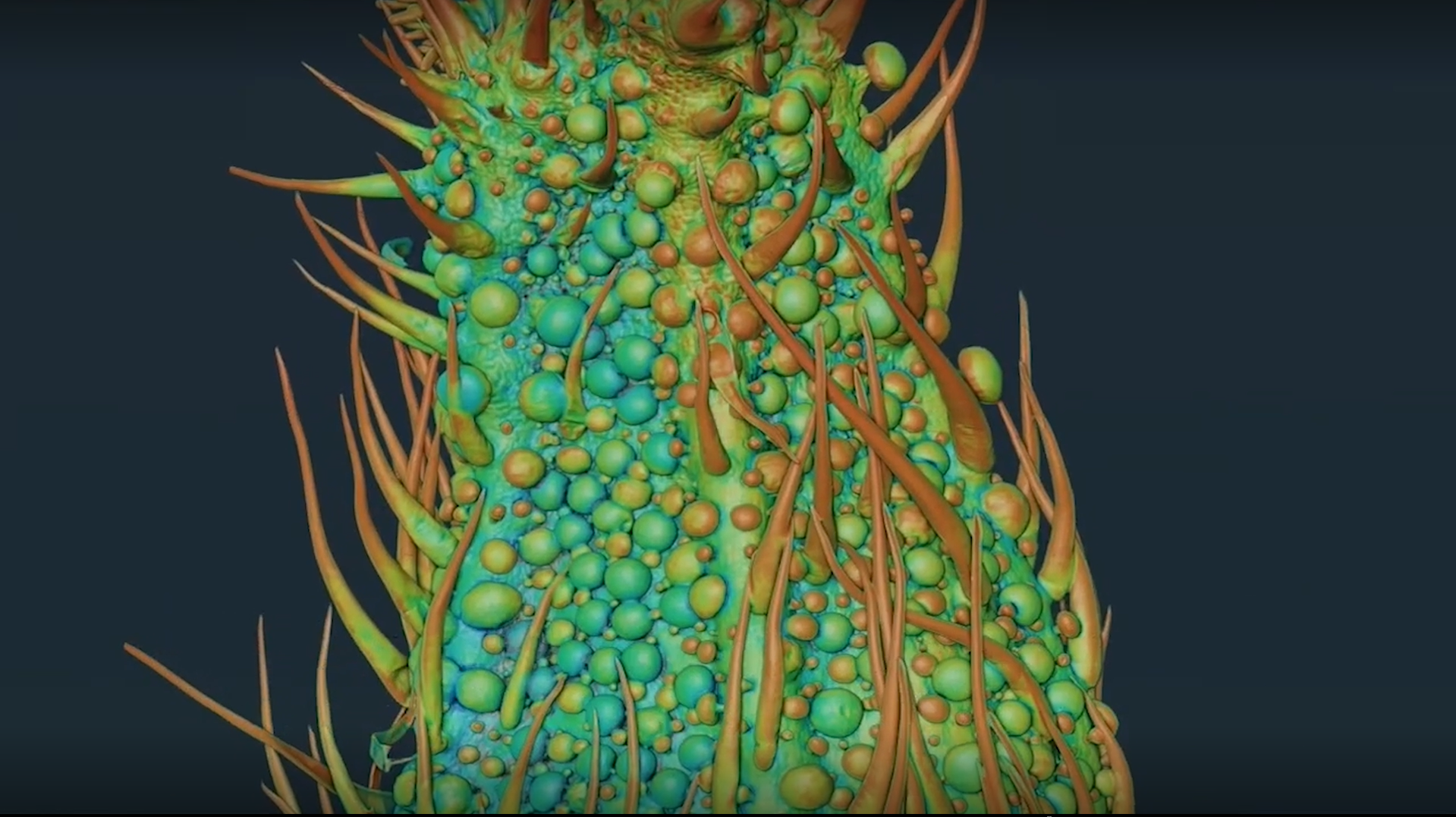
Capturing cannabis images that were previously impossible
The images produced by the CLS beamline are so detailed that they allow researchers to view all of the trichomes on the female flower while still intact. Trichomes are small sacs on the plant that contain active compounds such as cannabidiol (CBD) and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). According to Quilichini, the trichomes are very sensitive and easily break, but the new imaging technology can capture images that normal microscopes cannot come close to. By analyzing the trichomes at different phases of the plant’s development, the research team discovered that the amount and types of trichomes vary significantly during the plant’s growth cycle.
Improving cannabis cultivation practices and chemical diversity
The research is expected to have a significant impact on cannabis breeding and cultivation practices. By understanding the chemical composition of the plant at different stages of its growth, researchers can optimize cultivation techniques to achieve specific chemical profiles. For example, by selecting plants based on the desired chemical outcome, it may be possible to greatly increase the chemical diversity of the cannabis plant and even discover new applications for the plant beyond THC maximization.
Impact on related plants
Research on cannabis also has implications for other related plants such as lavender, mint, and tomatoes. Lavender and mint are known to produce similar compounds to cannabis, and research on these plants could help develop new pharmaceuticals or perfumes. Similarly, understanding the chemical makeup of tomatoes could help develop better-tasting varieties.
Conclusion
The new imaging technology developed by the Canadian Light Source represents a significant step forward in cannabis research. By capturing highly detailed images of the plant, researchers can now better understand the chemical composition of the plant and optimize cultivation techniques to achieve specific chemical outcomes. This could greatly increase the chemical diversity of the cannabis plant and potentially lead to the discovery of new applications for the plant beyond THC maximization. Furthermore, the impact of this research could extend to related plants, such as lavender, mint, and tomatoes, which could benefit from similar research.
FAQs
- What are trichomes, and why are they important in cannabis research? Trichomes are small sacs on the cannabis plant that contain active compounds such as CBD and THC. They are important in cannabis research because they are the primary source of these compounds.
- How does the new imaging technology work? The new imaging technology uses the BXDS High Energy Wiggler Beamline and Mid-IR Beamline at the Canadian Light Source’s synchrotron to capture highly detailed images of the cannabis plant.
- What are the implications of this research for cannabis breeding and cultivation practices? By understanding the chemical composition of the plant at different stages of its growth, researchers can optimize cultivation techniques to achieve specific chemical profiles, which could greatly increase the chemical diversity of the cannabis plant and potentially lead to the discovery of new applications for the plant beyond THC maximization.
- What other plants could benefit from similar research? Plants such as lavender, mint, and tomatoes are known to produce similar compounds to cannabis and could benefit from similar research.


COMMENTS